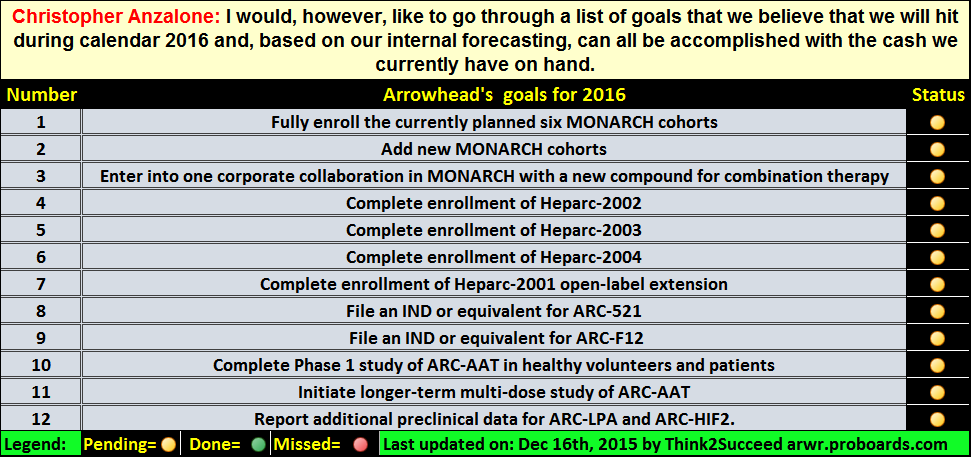
Post by partimefriend on Mar 21, 2020 10:15:55 GMT -5
wap.ulabmed.com/content-134-5342-1.html. 
Yinuo MedicineBack to Home
APASL2020: Results of ARO HBV (JNJ-3989) and NA Expansion Cohort Announced
2020-03-15 Source: Medical Connaught Medical Research: Slightly Xiao Xue
ARO HBV (JNJ-3989) is an RNAi therapy drug jointly developed by Arrowhead and Janssen. ARO HBV (JNJ-3989) can silence HBV RNA transcription from free cccDNA and integrated HBV DNA.
Phase 2a AROHBV1001 studies have been performed, which show that the combination of JNJ-3989 and nucleoside (acid) analogs (NA) for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B can reduce the level of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) by ≥1 log IU / mL, which can The detected virus products were reduced and well tolerated.
Recently at the 2020 Asia-Pacific Liver Diseases Annual Conference (APASL2020) held in Bali, Indonesia, researchers such as Professor Gane of New Zealand reported an enlarged cohort of 100-400 mg JNJ-3989, that is, two additional lower dose (25 and 50 mg) cohorts The results of the study.
The study included treated or untreated patients with HBeAg-positive or negative chronic hepatitis B. Subjects received 3 doses of JNJ-3989 subcutaneous injections (25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg, 200 mg, 300 mg, and 300 mg on days 1, 27, and 57). 400 mg). Patients started or continued treatment with nucleoside (acid) analogs (NA) (day 1) and continued to use nucleoside (acid) analogs (NA) throughout the study period. The study mainly evaluates the safety of JNJ-3989 + NA combination therapy and changes in virological parameters such as HBsAg, HBeAg, HBV DNA, HBV RNA, and HBV core-associated antigen (HBcrAg).
The results of the study showed that there were no patient discontinuations or serious drug-related adverse events throughout the study. At day 113 (the typical average low point after applying 3 doses of JNJ-3989, the 56th day after the last dose), the HBsAg levels from day 1 (8 cases) decreased by 1.00 ± 0.18 log10 IU / mL (25 mg ), 1.18 ± 0.08 log10 IU / mL (50 mg), 1.54 ± 0.18 log10 IU / mL (100 mg), 1.77 ± 0.18 log10 IU / mL (200 mg, 7 cases), 1.48 ± 0.11 log10 IU / mL (300 mg) and 1.75 ± 0.16 log10 IU / mL (400 mg) (pictured).
4/8 (25 mg), 5/8 (50 mg), 7/8 (100 mg), 8/8 (200 mg), 8/8 (300 mg), and 8/8 (400 mg) patients HBsAg levels reached a decrease of ≥1.0 log10 IU / mL from day 1 to the lowest point.
For patients with HBsAg levels greater than 100 IU / mL on day 1, on day 113, each group had 2/7 (25 mg), 3/8 (50 mg), 5/7 (100 mg), and 6/6 ( 200 mg), 6/8 (300 mg), and 5/7 (400 mg) patients achieved HBsAg levels of less than 100 IU / mL. The HBV DNA, HBV RNA, HBeAg, and HBcrAg levels of treated patients decreased.
In summary, the study concluded that patients with chronic hepatitis B who took three doses of JNJ-3989 (dose ranged from 25 to 400 mg once a month) were well tolerated in combination with nucleoside (acid) analogs (NA). Treatment with 100-400 mg of JNJ-3989, 97% (31/32) of patients can achieve a decrease in HBsAg level greater than or equal to 1.0 log IU / mL; 25 mg and 50 mg doses of JNJ-3989 are also active, but the same It is less effective than the higher dose group. (For more information on new drug research on liver disease, please pay attention to the "Liver Time" WeChat public account)!
Source: 2020APASL Proceedings Abstract # 777

Yinuo MedicineBack to Home
APASL2020: Results of ARO HBV (JNJ-3989) and NA Expansion Cohort Announced
2020-03-15 Source: Medical Connaught Medical Research: Slightly Xiao Xue
ARO HBV (JNJ-3989) is an RNAi therapy drug jointly developed by Arrowhead and Janssen. ARO HBV (JNJ-3989) can silence HBV RNA transcription from free cccDNA and integrated HBV DNA.
Phase 2a AROHBV1001 studies have been performed, which show that the combination of JNJ-3989 and nucleoside (acid) analogs (NA) for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B can reduce the level of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) by ≥1 log IU / mL, which can The detected virus products were reduced and well tolerated.
Recently at the 2020 Asia-Pacific Liver Diseases Annual Conference (APASL2020) held in Bali, Indonesia, researchers such as Professor Gane of New Zealand reported an enlarged cohort of 100-400 mg JNJ-3989, that is, two additional lower dose (25 and 50 mg) cohorts The results of the study.
The study included treated or untreated patients with HBeAg-positive or negative chronic hepatitis B. Subjects received 3 doses of JNJ-3989 subcutaneous injections (25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg, 200 mg, 300 mg, and 300 mg on days 1, 27, and 57). 400 mg). Patients started or continued treatment with nucleoside (acid) analogs (NA) (day 1) and continued to use nucleoside (acid) analogs (NA) throughout the study period. The study mainly evaluates the safety of JNJ-3989 + NA combination therapy and changes in virological parameters such as HBsAg, HBeAg, HBV DNA, HBV RNA, and HBV core-associated antigen (HBcrAg).
The results of the study showed that there were no patient discontinuations or serious drug-related adverse events throughout the study. At day 113 (the typical average low point after applying 3 doses of JNJ-3989, the 56th day after the last dose), the HBsAg levels from day 1 (8 cases) decreased by 1.00 ± 0.18 log10 IU / mL (25 mg ), 1.18 ± 0.08 log10 IU / mL (50 mg), 1.54 ± 0.18 log10 IU / mL (100 mg), 1.77 ± 0.18 log10 IU / mL (200 mg, 7 cases), 1.48 ± 0.11 log10 IU / mL (300 mg) and 1.75 ± 0.16 log10 IU / mL (400 mg) (pictured).
4/8 (25 mg), 5/8 (50 mg), 7/8 (100 mg), 8/8 (200 mg), 8/8 (300 mg), and 8/8 (400 mg) patients HBsAg levels reached a decrease of ≥1.0 log10 IU / mL from day 1 to the lowest point.
For patients with HBsAg levels greater than 100 IU / mL on day 1, on day 113, each group had 2/7 (25 mg), 3/8 (50 mg), 5/7 (100 mg), and 6/6 ( 200 mg), 6/8 (300 mg), and 5/7 (400 mg) patients achieved HBsAg levels of less than 100 IU / mL. The HBV DNA, HBV RNA, HBeAg, and HBcrAg levels of treated patients decreased.
In summary, the study concluded that patients with chronic hepatitis B who took three doses of JNJ-3989 (dose ranged from 25 to 400 mg once a month) were well tolerated in combination with nucleoside (acid) analogs (NA). Treatment with 100-400 mg of JNJ-3989, 97% (31/32) of patients can achieve a decrease in HBsAg level greater than or equal to 1.0 log IU / mL; 25 mg and 50 mg doses of JNJ-3989 are also active, but the same It is less effective than the higher dose group. (For more information on new drug research on liver disease, please pay attention to the "Liver Time" WeChat public account)!
Source: 2020APASL Proceedings Abstract # 777